Apoptosom Inhaltsverzeichnis Eigenschaften | Geschichte | Literatur | Einzelnachweise |...
ProteinkomplexApoptose
KofferwortaltgriechischProteinkomplexApoptoseBindungAktivierungPro-Caspase 9mitochondrialenCytochrom cZytosolApaf-1AdenosintriphosphatProteindomänenAminosäureAsp-315autoproteolysiertallosterischPro-Caspase 3Pro-Caspase 7
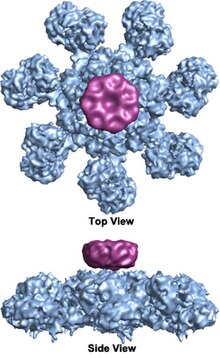
Apoptosom mit CARD
Ein Apoptosom (Kofferwort aus altgriechisch apóptosis ‚Niedergang‘ und soma ‚Körper‘) ist ein Proteinkomplex, der während des programmierten Zelltods (Apoptose) gebildet wird und der Bindung und Aktivierung der Pro-Caspase 9 dient.
Inhaltsverzeichnis
1 Eigenschaften
2 Geschichte
3 Literatur
4 Einzelnachweise
Eigenschaften |
Im Zuge des mitochondrialen Signalwegs der Apoptose wird beim Menschen Cytochrom c aus dem Mitochondrium ins Zytosol freigesetzt.[1] Dort bindet es zur Einleitung der Bildung des Apoptosoms an Apaf-1 (englisch apoptotic protease-activating factor 1 ‚apoptotischer Protease-aktivierender Faktor 1‘), welches auch Adenosintriphosphat (ATP) bindet.[2] Nach der Bindung lagern sich sechs weitere Apaf-1-Moleküle unter ATP-Verbrauch zu einer Scheibe. Daraufhin binden die CARD-Proteindomänen (englisch caspase recognition domain ‚Caspase Erkennungsdomäne‘) der Pro-Caspase 9 und des Apaf-1 aneinander und die gebundenen Procaspase-9-Moleküle werden zu Caspase-9-Molekülen nach der Aminosäure Asp-315 autoproteolysiert ebenso wie allosterisch durch Bindung des Apoptosoms aktiviert.[3][4] Die aktivierte Caspase 9 proteolysiert die Pro-Caspase 3 und Pro-Caspase 7 in ihre aktiven Formen.
Geschichte |
Die Bezeichnung Apoptosom wurde 1998 von Yoshihide Tsujimoto geprägt.[5] Die Bestandteile des Apoptosoms wurden 1999 von H. Zou und Kollegen beschrieben.[6]
Literatur |
- S. Yuan, C. W. Akey: Apoptosome structure, assembly, and procaspase activation. In: Structure (London, England: 1993). Band 21, Nummer 4, April 2013, S. 501–515, doi:10.1016/j.str.2013.02.024, PMID 23561633, PMC 3644875 (freier Volltext).
- S. Yuan, X. Yu, M. Topf, S. J. Ludtke, X. Wang, C. W. Akey: Structure of an apoptosome-procaspase-9 CARD complex. In: Structure (London, England: 1993). Band 18, Nummer 5, Mai 2010, S. 571–583, doi:10.1016/j.str.2010.04.001, PMID 20462491, PMC 2874686 (freier Volltext).
Einzelnachweise |
↑ H. H. Park: Structural features of caspase-activating complexes. In: International journal of molecular sciences. Band 13, Nummer 4, 2012, S. 4807–4818, doi:10.3390/ijms13044807, PMID 22606010, PMC 3344246 (freier Volltext).
↑ T. F. Reubold, S. Eschenburg: A molecular view on signal transduction by the apoptosome. In: Cellular signalling. Band 24, Nummer 7, Juli 2012, S. 1420–1425, doi:10.1016/j.cellsig.2012.03.007, PMID 22446004.
↑ Q. Hu, D. Wu, W. Chen, Z. Yan, Y. Shi: Proteolytic processing of the caspase-9 zymogen is required for apoptosome-mediated activation of caspase-9. In: The Journal of biological chemistry. Band 288, Nummer 21, Mai 2013, S. 15142–15147, doi:10.1074/jbc.M112.441568, PMID 23572523, PMC 3663534 (freier Volltext).
↑ S. B. Bratton, G. S. Salvesen: Regulation of the Apaf-1-caspase-9 apoptosome. In: Journal of cell science. Band 123, Pt 19Oktober 2010, S. 3209–3214, doi:10.1242/jcs.073643, PMID 20844150, PMC 2939798 (freier Volltext).
↑ Y. Tsujimoto: Role of Bcl-2 family proteins in apoptosis: apoptosomes or mitochondria? In: Genes to cells: devoted to molecular & cellular mechanisms. Band 3, Nummer 11, November 1998, S. 697–707, PMID 9990505.
↑ H. Zou, Y. Li, X. Liu, X. Wang: An APAF-1.cytochrome c multimeric complex is a functional apoptosome that activates procaspase-9. In: The Journal of biological chemistry. Band 274, Nummer 17, April 1999, S. 11549–11556, PMID 10206961.